How Is Computer Science Related To Climate Change
The Earth's Climate
Climate change is altering temperature, precipitation, and sea levels, and will adversely impact human and natural systems, including water resources, human settlements and wellness, ecosystems, and biodiversity. The unprecedented acceleration of climate change over the final 50 years and the increasing conviction in global climate models add to the compelling bear witness that climate is being affected past greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities.two
Changes in climate should not be confused with changes in weather. Weather is observed at a particular location on a time scale of hours or days, and exhibits a high degree of variability, whereas climate is the long-term boilerplate of brusk-term weather patterns, such equally the almanac boilerplate temperature or rainfall.3 Under a stable climate, there is an energy remainder between incoming brusk moving ridge solar radiations and outgoing long moving ridge infrared radiation. Solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and about is absorbed by the Earth's surface. The surface and then re-emits energy as infrared radiation, a portion of which escapes into space. Increases in the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the temper reduce the amount of free energy the Earth'due south surface radiates to space, thus warming the planet.4
The Globe's Greenhouse Effecti

Climate Forcings
- Disturbances of the Earth's balance of incoming and outgoing energy are referred to as positive or negative climate forcings. Positive forcings, such every bit GHGs, exert a warming influence on the Globe, while negative forcings, such every bit sulfate aerosols, exert a cooling influence.5
- Increased concentrations of GHGs from anthropogenic sources have increased the absorption of infrared radiation, enhancing the natural greenhouse consequence. Marsh gas and other GHGs are more potent, only CO2 contributes nearly to warming because of its prevalence.5
- Anthropogenic GHG emissions, to date, amount to a climate forcing roughly equal to 1% of the net incoming solar free energy, or the free energy equivalent of burning xiii million barrels of oil every infinitesimal.half dozen
Climate Feedbacks and Inertia
- Climate alter is also affected by the World'south responses to forcings, known every bit climate feedbacks. For instance, the increase in h2o vapor that occurs with warming further increases climate forcing and evaporation, equally water vapor is a powerful GHG.5
- The volume of the ocean results in large thermal inertia that slows the response of climate change to forcings; energy balance changes issue in delayed climate response with high momentum.seven
- Every bit polar water ice melts, less sunlight is reflected and the oceans blot more solar radiation.5
- Due to increasing temperature, large reserves of organic affair frozen in subarctic permafrost volition thaw and decay, releasing additional COii and methane to the atmosphere.eightJune 2020 was tied for the warmest on record and extreme temperatures in the Artic (especially Siberia) contributed to big wildfires and farther thawing of permafrost. The fires alone were estimated to have released 59 MMT of CO2 into the atmosphere.9
- If GHG emissions were completely eliminated today, climate modify impacts would yet continue for centuries.ten The Globe's temperature requires 25 to l years to achieve 60% of its equilibrium response.xi
- Today'southward emissions volition touch on future generations; CO2 persists in the temper for hundreds of years.12
Human Influence on Climate
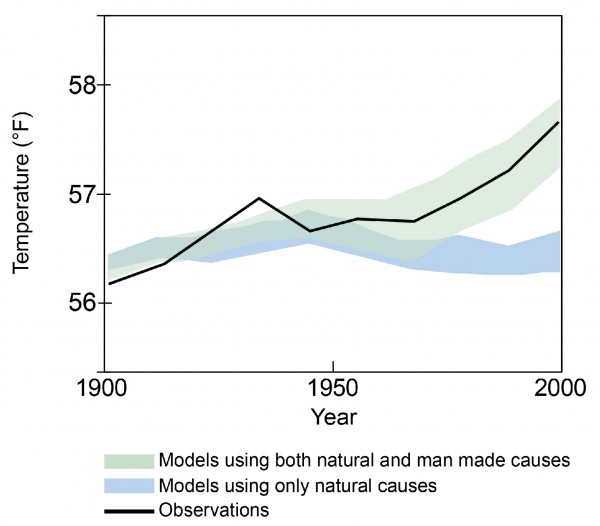
- Separately, neither natural forcings (e.g., volcanic action and solar variation) nor anthropogenic forcings (e.m., GHGs and aerosols) tin fully explain the warming experienced since 1850.13
- Climate models nearly closely match the observed temperature trend just when natural and anthropogenic forcings are considered together.thirteen
- In 2013, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Alter (IPCC) concluded that: "Information technology is extremely likely (>95 % certainty) that homo influence has been the dominant crusade of the observed warming since the mid-20th century."5
Modeled and Observed Global Average Temperatures14
Observed Impacts
Physical Systems
- Global average temperature was 0.98oC (i.76oF) higher in 2020 than in the belatedly 1800s.15
- The warmest year on record since records began in 1880 was 2016, with 2020 ranking second. In 2020 global boilerplate land temperatures experienced a record high, while 2016 global ocean temperatures remain the highest on record. The seven warmest years since 1880 have all occurred since 2014 and in 2020 annual global temperatures were above boilerplate for the 44th sequent yr.xv
- Annual 2020 arctic temperatures rose to 1.9oC above the 1981-2010 average. Chill sea water ice is becoming younger, thinner, and less expansive. The 2020 extent of ice reached the 2d lowest almanac cover on record since 1979, 3.74 one thousand thousand square kilometers.16
- U.S. boilerplate almanac precipitation has increased by 4% since 1901, just the intensity and frequency of extreme atmospheric precipitation events has increased even more, a trend that is expected to go on.17
- In the 20th century, global hateful sea level rose between 17 and 21 cm, subsequently having been quite stable over the previous several thousand years.5
- Snow cover has noticeably decreased in the Northern Hemisphere. From 1967-2012, snow cover extent decreased past approximately 53% in June, and effectually seven% in March and April.five
Northwestern Glacier melt, Alaska, 1940-200518

Biological Systems
- Warming that has already occurred is affecting the biological timing (phenology) and geographic range of plant and animal communities.xix Relationships such as predator-prey interactions are affected by these shifts, peculiarly when changes occur unevenly betwixt species.xx
- Since the beginning of the 20th century, the boilerplate growing season in the contiguous 48 states has lengthened past nearly two weeks.21
Predicted Changes
Increased Temperature
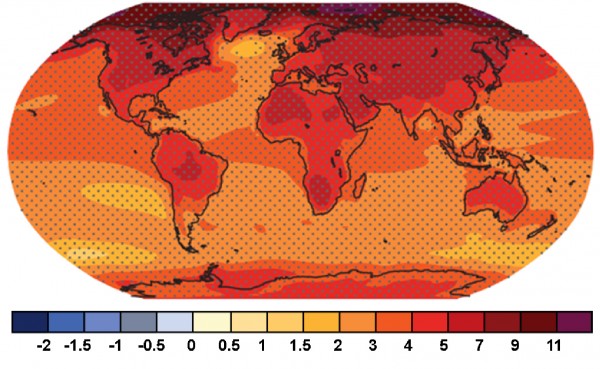
- By 2035, IPCC predicts that the temperature will rise between 0.3-0.viioC (0.five-1.3oF). In the long term, global mean surface temperatures are predicted to rise 0.4-2.half dozenoC (0.7-4.viioF) from 2045-2065 and 0.3-4.8oC (0.5-8.half dozenoF) from 2081-2100, relative to the reference period of 1986-2005. Since 1970, global average temperatures accept been rising at a rate of 1.7oC per century, significantly higher than the average rate of decline of 0.01oC over the past 7,000 years.v,22
- A warming planet does not simply outcome in college average daytime temperatures, the frequency and magnitude of extreme hot days will increase.22
Projected Annual Mean Modify in Temperature (°C), 21st Century5
Ocean Impacts
- Models anticipate body of water level rise between 26 and 77 cm for a 1oC increase in temperature. The ascension will be a result of thermal expansion from warming oceans and boosted water added to the oceans by melting glaciers and ice sheets.22
- The oceans absorb about 27% of anthropogenic COtwo emissions, resulting in increased acidity. Even under bourgeois projections, coral reefs will be severely impacted.23
Implications for Homo and Natural Systems
- Impacts of climatic change will vary regionally merely are very probable to impose costs that will increment equally global temperatures increase.10
- This century, an unprecedented combination of climate change, associated disturbances, and other global change drivers will probable exceed many ecosystems' capacities for resilience.24 Species extinction, food insecurity, human activeness constraints, and limited adaptability are risks associated with warming at or above predicted temperatures for the yr 2100 (fouroC or 7oF higher up pre-industrial levels).10
- With an increase in average global temperatures of 2oC, nigh every summer would be warmer than the hottest 5% of contempo summers.25
- Due to regional variation, a 2-foot rise in sea level would crusade relative increases of 3.5 feet in Galveston, TX and ane foot in Neah Bay, WA.two
- Increased temperatures, changes in precipitation and climate variability would alter the geographic ranges and seasonality of diseases spread by organisms like mosquitoes.25
- Although higher CO2 concentrations and slight temperature increases can boost crop yields, the negative furnishings of warming on found health and soil moisture pb to lower yields at higher temperatures. Intensified soil and water resource deposition resulting from changes in temperature and precipitation will further stress agriculture in sure regions.25
Cite as:
Center for Sustainable Systems, Academy of Michigan. 2021. "Climatic change: Scientific discipline and Impacts Factsheet." Pub. No. CSS05-xix.
Source: https://css.umich.edu/factsheets/climate-change-science-and-impacts-factsheet
Posted by: hardydocketook.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Is Computer Science Related To Climate Change"
Post a Comment